Troubleshooting Microsoft Graph App Registration Errors
Troubleshooting Microsoft Graph App Registration Errors
Welcome back! This is the third post in my series on automation in Microsoft Graph and the AdminService using PowerShell. This post is intended as a follow up to my last post, Connecting to Microsoft Graph with PowerShell. While I was writing my last post, I ran into a few issues while creating the App Registration to connect to Microsoft Graph. In this post I will provide a few things I found that may help you with troubleshooting your applications.
If you followed the steps in my last post, you shouldn’t run into any issues, but just in case you do – here are a few items you can try:
No Reply Address or The Reply URL does not match
When you are using interactive authentication, you may receive a message that looks like this:
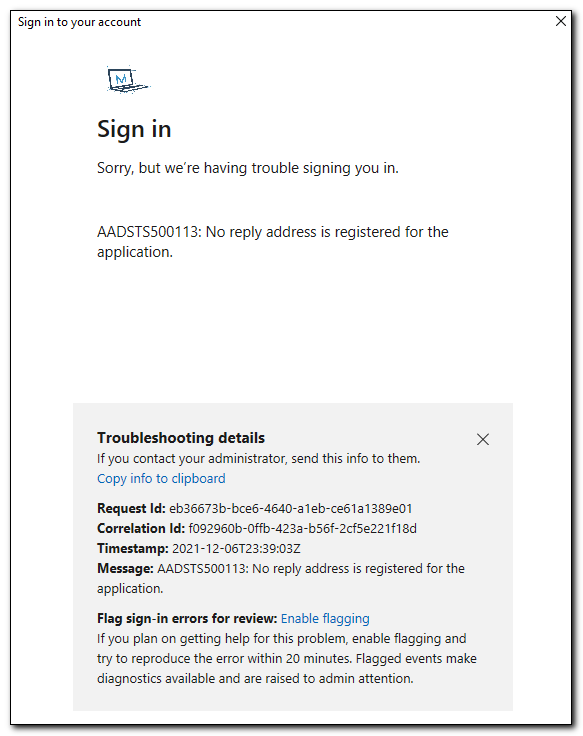
The error message in this response is: AADSTS500113: No reply address is registered for the application.
You may also see the following error in PowerShell:

The full text of this error is:
Get-MsalToken : A configuration issue is preventing authentication - check the error message from the server for details. You can modify the configuration in the application registration portal. See https://aka.ms/msal-net-invalid-client for details. Original exception: AADSTS50011: The reply URL specified in the request does not match the
reply URLs configured for the application:
Both errors are pointing to the same issue. The Reply URL in the App Registration is incorrect. To correct these, open Azure Active Directory and go to App Registration. Open the App Registration for your application. Click on Authentication in the menu on the left-hand side.
It should be configured to use the “Mobile and desktop applications” platform and have the redirect URL https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient checked.
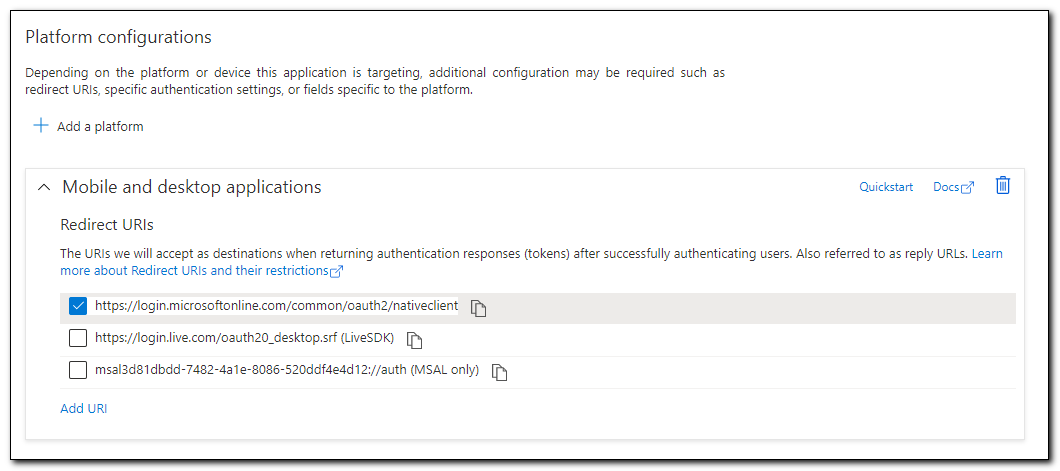
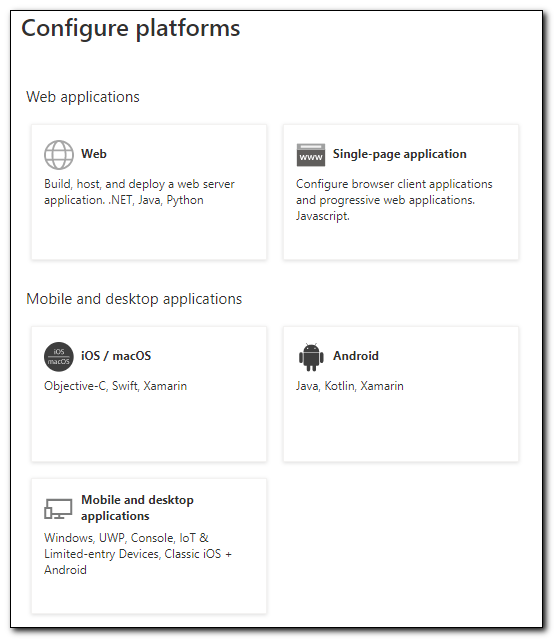
If this box is not checked, check it. If the Mobile and desktop applications platform is not visible, click on “Add a Platform.” On the platforms tab select “Mobile and desktop applications.”
Check the box for https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient and click Configure.
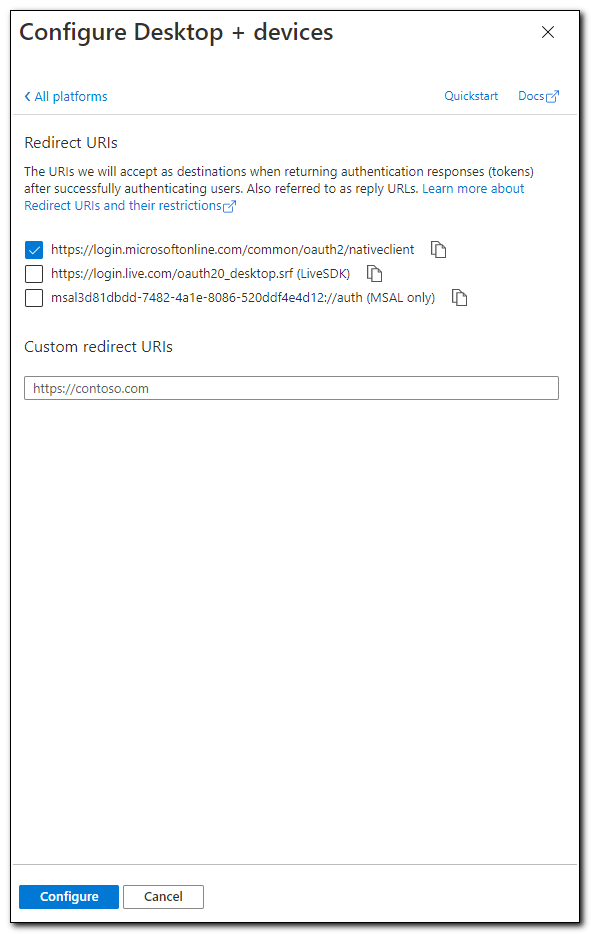
Test again. If this was the only issue in your application, you should be able to connect and get an authorization token.
The request body must contain the following parameter: ‘client_assertion or ‘client secret’
Once the correct Reply/Redirect URLs are configured, I ran into another issue. This time my error message changed. The new error message wasn’t as simple, and it was a little more difficult to track down the resolution. In this case, I got the following error message:

The full text of the error is:
Get-MsalToken : A configuration issue is preventing authentication - check the error message from the server for details. You can modify the configuration in the application registration portal. See https://aka.ms/msal-net-invalid-client for details. Original exception: AADSTS7000218: The request body must contain the following parameter:
'client_assertion' or 'client_secret'.
To correct this error, there are two places to check. First, check to see if the application is configured to allow Public Client flows. Like the Reply URLs listed above this issue is correct on the Authentication page of the App Registration. Scroll down to the bottom of the page.
Under “Allow public client flows,” move the “Enable the following mobile and desktop flows” slider to Yes.

You can also check the App manifest. The manifest should match the setting above. If enabling mobile and desktop flow does not fix the issue click “Manifest” in the menu. The value allowpublicclient should be set to true.
{
"allowPublicClient": true,
}
Error 403: Forbidden
Finally, once you have connected to Microsoft Graph with PowerShell and perform an API call, there are any number of different errors you may get in response. I won’t go into all of them here, but I did want to call out one specific error. Error 403: Forbidden is a standard web response when we don’t have access to a specific resource. In this case, it is caused directly by a misconfiguration in our application. We need to make sure our application has the correct API permissions to be able to access the resources we are trying to interact with.
App registrations have User.read permissions by default. In this case, I was able to connect to Microsoft Graph and return my user object when testing, however, as soon as I tried returning a list of devices, I received a 403 response.
The API call I made was the following:
$AccessToken = $Auth.AccessToken
#graph
$graphGetParams = @{
Headers = @{
"Content-Type" = "application/json"
"Authorization" = "Bearer $($AccessToken)"
}
Method = "GET"
ErrorAction = "SilentlyContinue"
URI = "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/deviceManagement/managedDevices"
}
Invoke-RestMethod @graphGetParams
In this case, I was passing the Access Token from Get-MSALToken into the Invoke-RestMethod cmdlet. I know I have a valid access token, so I expected it would return a list of managed devices from Microsoft Graph. Instead, I received the following response:
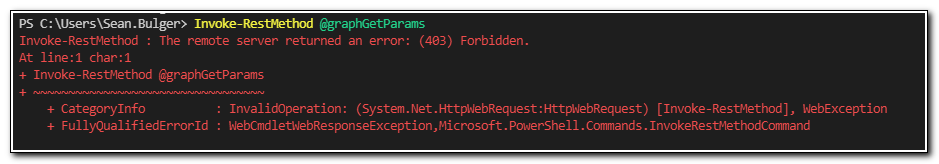
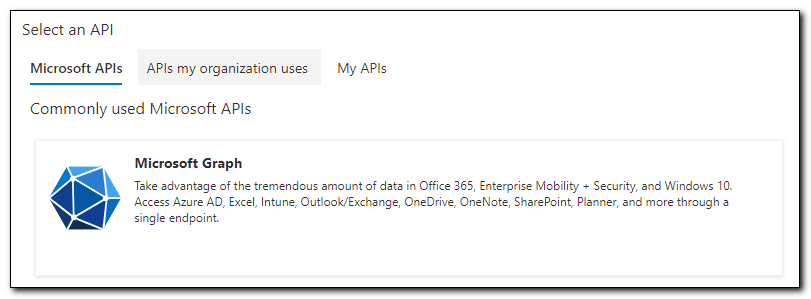
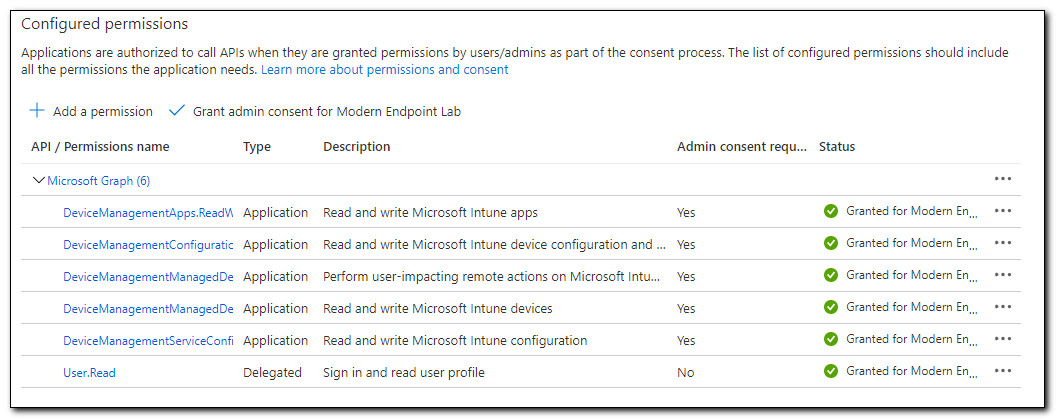
To correct this issue, I need to add the appropriate API permissions to my application registration. Go to the “API permissions” page inside of the App Registration. Click “Add a permission.” Select Microsoft Graph.
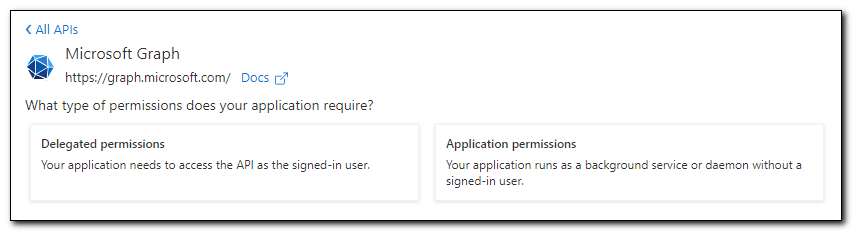
We will select either delegated or application permission based on how we want to access data. If we want to access data on behalf of an interactively logged in user, we will select “Delegated permissions,” if the application will act as a service, we need to select “Application permissions.”
Search for Device and select the permissions you want the application to have.
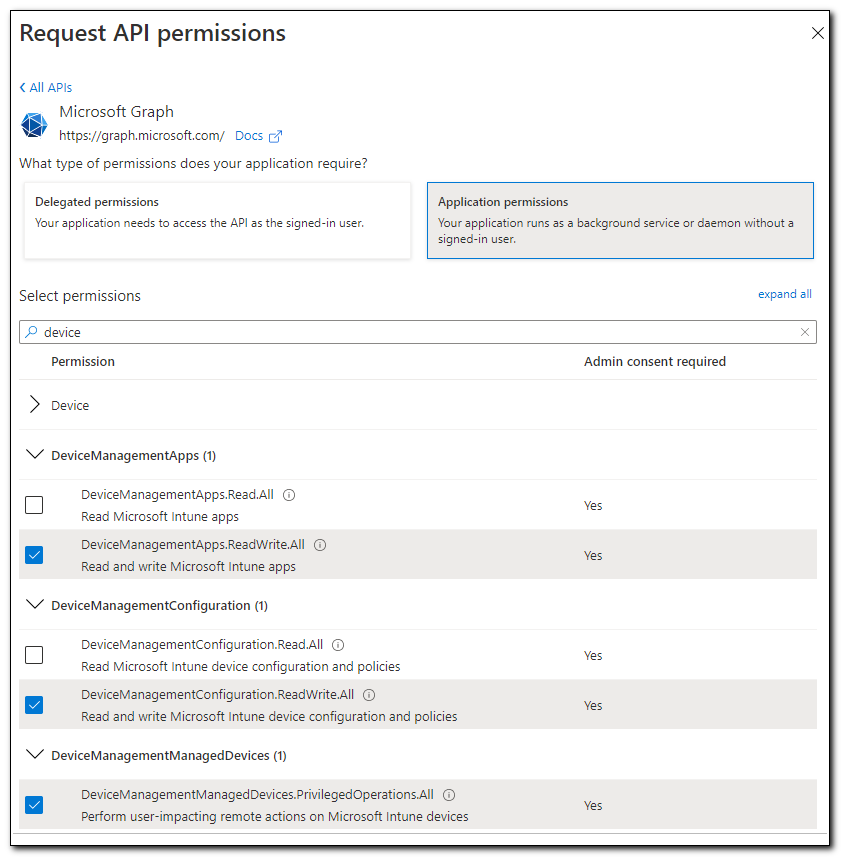
In this instance, I wan to give the app the following permissions. After selected the permissions click “Add Permissions:”
DeviceManagementApps.ReadWrite.All
DeviceManagementConfiguration.ReadWrite.All
DeviceManagementManagedDevices.PrivilegedOperations.All
DeviceManagementManagedDevices.ReadWrite.All
DeviceManagementServiceConfig.ReadWrite.All
On the API Permissions screen click on “Grant Admin Consent for….” To grant consent to all the requested permissions. The status should show a green check mark and say “Granted for …”
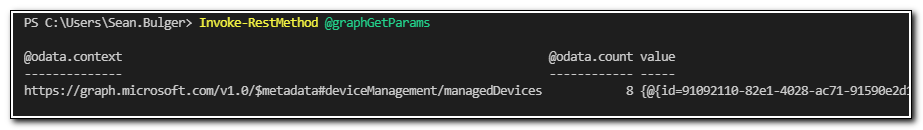
The access token includes information about the API permissions that an application has been granted. You will need to request a new token before you can try the API call again. After running get-MSALToken in the appropriate context we can try our API call to return devices again. This time, we get a response:
This only covers a few issues I ran into while creating the App Registrations I used in my previous blog post. I know that there are a lot of other possible responses. If you know of any other issues I should cover, please feel free to share them!
Follow the full series below:
- Everything I wanted to know about APIs but was afraid to ask
- Connecting to Microsoft Graph with PowerShell
- Troubleshooting Microsoft Graph App Registration Errors
- Defining a script and finding the Microsoft Graph Calls
- Splatting with Invoke-RestMethod in PowerShell
- Updating Device Management name in PowerShell with Microsoft Graph
- Surprise Post:Adding Filters to application assignments with PowerShell and Microsoft Graph
- Working with Azure Key Vault in PowerShell
- Creating an Azure Automation Account
- Setting up a Hybrid Worker on an Azure Arc Enabled Server
- Connecting an Azure Automation Account to the Configuration Manager AdminService
- Running an Azure Automation runbook to update MEMCM Primary User
- Using Power Automate to update MEMCM Device based on Intune User

